CSS
- Cascading Style Sheets is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language like HTML.
- CSS is a cornerstone technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and JavaScript.
- CSS: Cascading Style Sheets
- Developed by: Håkon Wium Lie; Bert Bos; World Wide Web Consortium
- Initial release: December 17, 1996
- There are 3 part of catagory

1.External Style Sheet
2.Inline
3.Internal Style Sheet
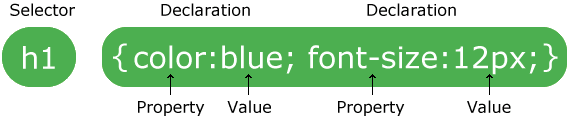
Structure Of CSS
Advantage of CSS
- Easier to maintain and update.
- Greater consistency in design.
- More formatting options.
- Lightweight code.
- Faster download times.
- Search engine optimization benefits.
- Ease of presenting different styles to different viewers.
- Greater accessibility.

- It cannot perform any logical operations like if/else, for/while, +/-, etc.
- You cannot read your files using CSS.
- Unable to interact with databases.
- CSS can't request a web page.
Example of CSS
<!DOCTYPE html><html>
<head>
<style>
p {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello World!</p>
<p>These paragraphs are styled with CSS.</p>
</body>
</html>
Keyword Of CSS

- E an element of type
- E:link an E element is the source anchor of a hyperlink of which the target is not yet visited (:link) or already visited (:visited)
- E:active an E element during certain user actions
- E::first-line the first formatted line of an E element
- E::first-letter the first formatted letter of an E element
- .c all elements with class="c"
- #myid the element with id="myid"
- E.warning an E element whose class is "warning" (the document language specifies how class is determined)
- E#myid an E element with ID equal to "myid"
- E F an F element descendant of an E element
- * any element
- E[foo] an E element with a "foo" attribute
- E[foo="bar"] an E element whose "foo" attribute value is exactly equal to "bar"
- E[foo~="bar"] an E element whose "foo" attribute value is a list of whitespace-separated values, one of which is exactly equal to "bar"
- E[foo|="en"] an E element whose "foo" attribute has a hyphen-separated list of values beginning (from the left) with "en"
- E:first-child an E element, first child of its parent
- E:lang(fr) an element of type E in language "fr" (the document language specifies how language is determined)
- E::before generated content before an E element's content
- E::after generated content after an E element's content
- E > F an F element child of an E element
- E + F an F element immediately preceded by an E element
- E[foo^="bar"] an E element whose "foo" attribute value begins exactly with the string "bar"
- E[foo$="bar"] an E element whose "foo" attribute value ends exactly with the string "bar"
- E[foo*="bar"] an E element whose "foo" attribute value contains the substring "bar"
- E:root an E element, root of the document
- E:nth-child(n) an E element, the n-th child of its parent
- E:nth-last-child(n) an E element, the n-th child of its parent, counting from the last one
- E:nth-of-type(n) an E element, the n-th sibling of its type
- E:nth-last-of-type(n) an E element, the n-th sibling of its type, counting from the last one
- E:last-child an E element, last child of its parent
- E:first-of-type an E element, first sibling of its type
- E:last-of-type an E element, last sibling of its type
- E:only-child an E element, only child of its parent
- E:only-of-type an E element, only sibling of its type
- E:empty an E element that has no children (including text nodes)
- E:target an E element being the target of the referring URI
- E:enabled a user interface element E that is enabled
- E:disabled a user interface element E that is disabled
- E:checked a user interface element E that is checked (for instance a radio-button or checkbox)
- E:not(s) an E element that does not match simple selector s
- E ~ F an F element preceded by an E element




No comments:
Post a Comment